|
Teaching Learning Process : |
|
|
|
Learning
strategies for students |
|
|
|
Previous
studies show that students depend upon their
senses to process knowledge around them.
Most of the successful learners tend to use
one of their senses more frequently than the
others. Over the last few years, the concept
of 'Preferred Learning Styles' has been
heavily criticised. According to recent
literature in the field of education, the
idea that a child has a learning style
preference is a myth. |
|
|
|
Visual Strategies:
|
|
|
|
Pupils learn
and retain the knowledge better when it is
presented to them in a pictorial form, such
as diagrams, charts, arrows and symbols.
This approach has been refined through the
research into dual coding. Using clear
visuals of information hierarchy as an
approach to teaching practices is an
accessible way of giving access to complex
regular content. To apply this approach into
the classroom management strategy, teachers
can apply the following in the classroom
learning environment: |
|
|
|
Use a wide
range of visual aids such as pictures,
charts, graphs, and illustrations; |
|
|
-
Include handouts and outlines for
teaching various academic concepts;
- Show
pictures and explain;
- Remove
potential distractions;
- Leave
some space in handouts where students
can write notes;
- Show
clear screens while using multimedia;
- Use
color full illustrations and
presentations.
|
|
Auditory strategies:
|
|
|
|
Creating
learning experiences that involve listening
and talking. Successful teachers need to
apply the following instructional methods in
their classroom: |
|
|
- Begin
new topic with the background of what
academic concepts are coming;
- Use
activities such as discussion groups or
brainstorming;
- Ask
the learners to read aloud the question;
- Have
learners sit in groups where vocal
collaboration is possible;
-
Conclude by summarizing what was taught.
|
|
Reading & Writing |
|
|
|
Using more
traditional instructional methods such as
rewriting their notes, reading textbooks,
and note-taking. They tend to learn better
by applying the following in their
classroom: |
|
|
-
They must
be provided with the written information
on worksheets, and other text-heavy
resources;
-
Ask
students to rewrite notes;
-
Using
bullet point lists;
-
Turning
charts and diagrams into words.
-
They must
be asked to reference written text.
|
|
Kinaesthetic
Learning |
|
|
|
Kinaesthetic
Learning [or embodied cognition] is also
referred to as tactile learning. Kinesthetic
learning is the most physical of all the
learning styles, as kinaesthetic or tactile
learners grasp information best through the
instructional strategy that involves the
practical strategy of motion, movement and
touch. The word kinaesthetic learners
indicate students' ability to sense movement
and body position in the learning
environment. Student understanding of
Tactile learners is enhanced by the physical
activity such as touching, feeling and
moving things. In recent years, the field of
embodied cognition has received a lot of
interest. The work of Barbara Tversky has
shown us that being referred to as a 'kinaesthetic
learner' probably describes most of us.
The following are a selection of strategies
used to teach kinaesthetic learners (or
anyone else for that matter!): |
|
|
-
Involve
physical movement in the teaching
methods;
-
Provide
hands-on experience to the learners;
-
Use
flashcards to teach;
-
Engage
students in classroom activities that
involve physical materials.
-
Ask
students to draw images of information
in the formative assessments.
|
Utilizing
multisensory approaches in the classroom
Other teaching and learning strategies you
should research
At Structural Learning, we have been trying
to uncover classroom ideas that are both
evidenced informed and easy to implement.
Organisations such as the EEF condense the
findings of studies of classroom
instruction. We can use this extensive
evidence to make better decisions about how
we can teach our lessons. Focusing on the
pedagogy is with the highest impact is a
good starting point for any school.
The strategies listed within these journals
help classroom practitioners widen their
range of skills. If you are thinking about
making some pedagogical changes across your
school, you may want to explore some of the
following topics: |
|
|
|
Integrating
formative assessment strategies in your
classroom. |
|
|
-
Advancing critical thinking skills by
using graphic organisers to help
students organise their thinking.
-
Provide playful learning experiences
that promote divergent thinking.
-
Utilize dual coding methods to make
curriculum content easier to understand.
-
Integrate responsive teaching as a whole
school philosophy.
- Build
the pillars of teaching by embracing
Rosenshine's principles of instruction.
-
Provide insightful student feedback that
moves their thinking forward.
-
Promote critical thinking skills by
using Oracy or dialogic teaching
methods.
- Make
abstract concepts in maths more concrete
by using physical materials.
-
Develop intervention lessons into
engaging experiences by using different
learning tools.
- Make
your assessment strategy more creative
by giving summative assessments less
priority.
- Only
embrace evidence-informed ideas that
have a clear impact.
|
|
|
|
Embrace evidence
informed teaching and learning |
|
|
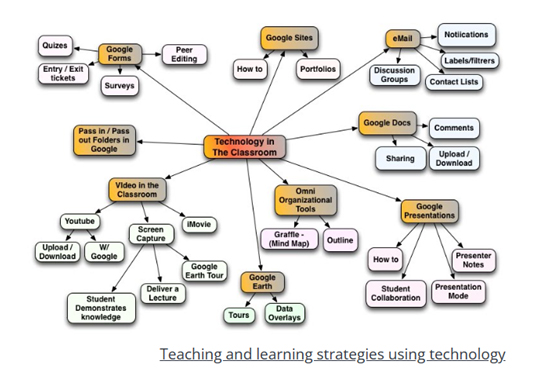
Integrating
Technology: Harnessing Digital Tools for
Enhanced Education
The integration of technology into the
educational landscape has opened the door to
a multitude of creative teaching strategies,
enabling teachers to craft immersive and
dynamic learning experiences for their
students.
Just as a chameleon adapts to its
surroundings, educators must harness digital
tools to facilitate personalized learning,
addressing the unique needs and abilities of
each individual. Through platforms that
support game-based learning and asynchronous
learning, students can engage with the
curriculum at their own pace, fostering a
sense of autonomy and ownership in their
educational journey.
By drawing on Jerome Bruner's concepts of
assimilation and accommodation, educators
can use technology to enhance
information-processing skills while also
providing experiential learning
opportunities.
This aligns with John Dewey's educational
philosophy, which emphasizes the importance
of learning through experience and
interaction with the environment.
Technology-based learning tools act as a
bridge between the abstract and the
concrete, allowing students to actively
engage with the subject matter and gain a
deeper understanding of complex concepts.
In order to maximize the potential of
technology for enhanced education, teachers
should remain open to exploring new digital
resources and incorporating them into their
pedagogical approach. Edutopia and the
International Society for Technology in
Education (ISTE) offer a wealth of resources
and strategies for effectively integrating
technology into the classroom, empowering
educators to elevate their teaching practice
and unlock their students' full potential. |
|
|
|
 |
|
|







